Time:2013-04-13ClickTimes:
Recently, professor Lixin Xiao and professor Qihuang Gong and collaborators
have designed a series of new electron transport materials for organic
light-emitting devices (OLEDs) and high performances have been achieved,
detailed results has been published in Adv. Funct. Mater. (2013, 23, 1323–1330).
OLED has been commercialized as flat panel display since 1997, but some
issues remain to be further developed. From the view point of the OLED materials
developed, the mobility of p-type material (hole transport) is much higher than
that of the n-type material (electron transport), and the former is about 1000
times higher. The lack of efficient electron transport material is the limit
factor of OLED efficiency, therefore the development of an electron transport
material is crucial to OLED.
They have paid a lot of efforts on how to improve the electron transport
properties of the organic materials and the development of efficient electron
transport material. Nearly 100% internal quantum efficiency of OLED has been
achieved by using the electron transport materials previously reported. In
addition to the hope that it can get high efficiency of the device for electron
transport material, its thermal stability is a very important issue which will
affect the lifetime of the device. Based on this consideration, we have
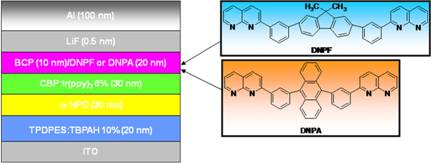
synthesized a series thermally stable naphthyridines derivatives, they are not
only highly efficient electron transport ability, and having a larger bandwidth
(2.94-3.33 eV), with respect to traditional electron transporting material such
as Alq3, has a very good exciton blocking ability, to thereby obtain a highly
efficient green phosphorescent OLED, indicate that them has great potential to
use as the electron transport material of the green phosphorescent device. The
device structure is shown in Figure 1.
|
The work was supported by the Creative Research Group Project of the National
Natural Science Foundation of China, and the National Basic Research Program of
China.
