Large-scale single layer and multilayer graphene are usually produced by
chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on transition metal substrates. The
advantages of the CVD method cover low preparation temperature, high
quality, scalable production, and easy transfer to other substrates. Among
few-layer graphene, bilayer (BLG) and trilayer graphene (TLG) are the most
extensively studied materials, partially due to the fact that there is an
electrically tunable band gap in BLG and ABC-stacked TLG and meanwhile the
carrier mobility is not degraded, which are critical for their application
in transistor. In addition, in an actual device, graphene has to be
contacted with metal electrode. Therefore, the interfacial properties of
B(T)LG and metal contacts should be clarified.
Using density functional theory with dispersion correction, the
Computational Materials Group led by Prof. Jing Lu at School of Physics,
Peking University provide the first systematic investigation on the
interfacial properties of bilayer and trilayer graphene on a variety of
metal substrates. Three categories of interfacial structures are revealed.
The adsorption of B(T)LG on Al, Ag, Cu, Au, and Pt substrates is a weak
physisorption, but a band gap can be opened. The adsorption of B(T)LG on Ti,
Ni, and Co substrates is a strong chemisorption, and a stacking-insensitive
band gap is opened for the two uncontacted layers of TLG. The adsorption of
B(T)LG on Pd substrate is a weaker chemisorption, with a band gap opened for
the uncontacted layers. This fundamental study also helps for B(T)LG device
study due to inevitable graphene/metal contact.
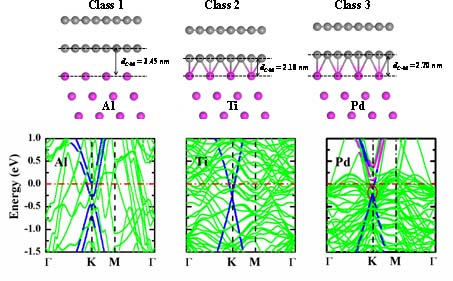
|
Representative geometries and electronic structures of three classes of
bilayer graphene/metal interfaces.
A band gap of 0.20, 0, and 0.12 eV is opened
for bilayer graphene on Al, Ti, and Pd substrates, respectively.
|
This work has been published on Scientific Reports (Interfacial Properties of
Bilayer and Trilayer Graphene on Metal Substrates, Scientific Reports 3, 2081
(2013); http://www.nature.com/srep/2013/130627/ srep02081/full/ srep02081). The
first co-authors of this paper are Zheng Jiaxin, a PhD student from Academy for
Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies and School of Physics in Peking University,
and Wang Yangyang, a PhD student from School of Physics in Peking University.
The collaborators include Prof. Gao Zhengxiang, Prof. Yu Dapeng, and Prof. Shi
Junjie from School of Physics, Peking University, and Prof. Mei Wai-Ning from
Department of Physics, University of Nebraska at Omaha.
The work was supported by the National 973 Projects, Program for New Century
Excellent Talents in University of MOE of China, NSFC, and the State Key
Laboratory for Artificial Microstructure and Mesoscopic Physics, Peking
University.
